Augmented Reality Transforms Travel Experiences


The Digital Layer Revolutionizing Exploration
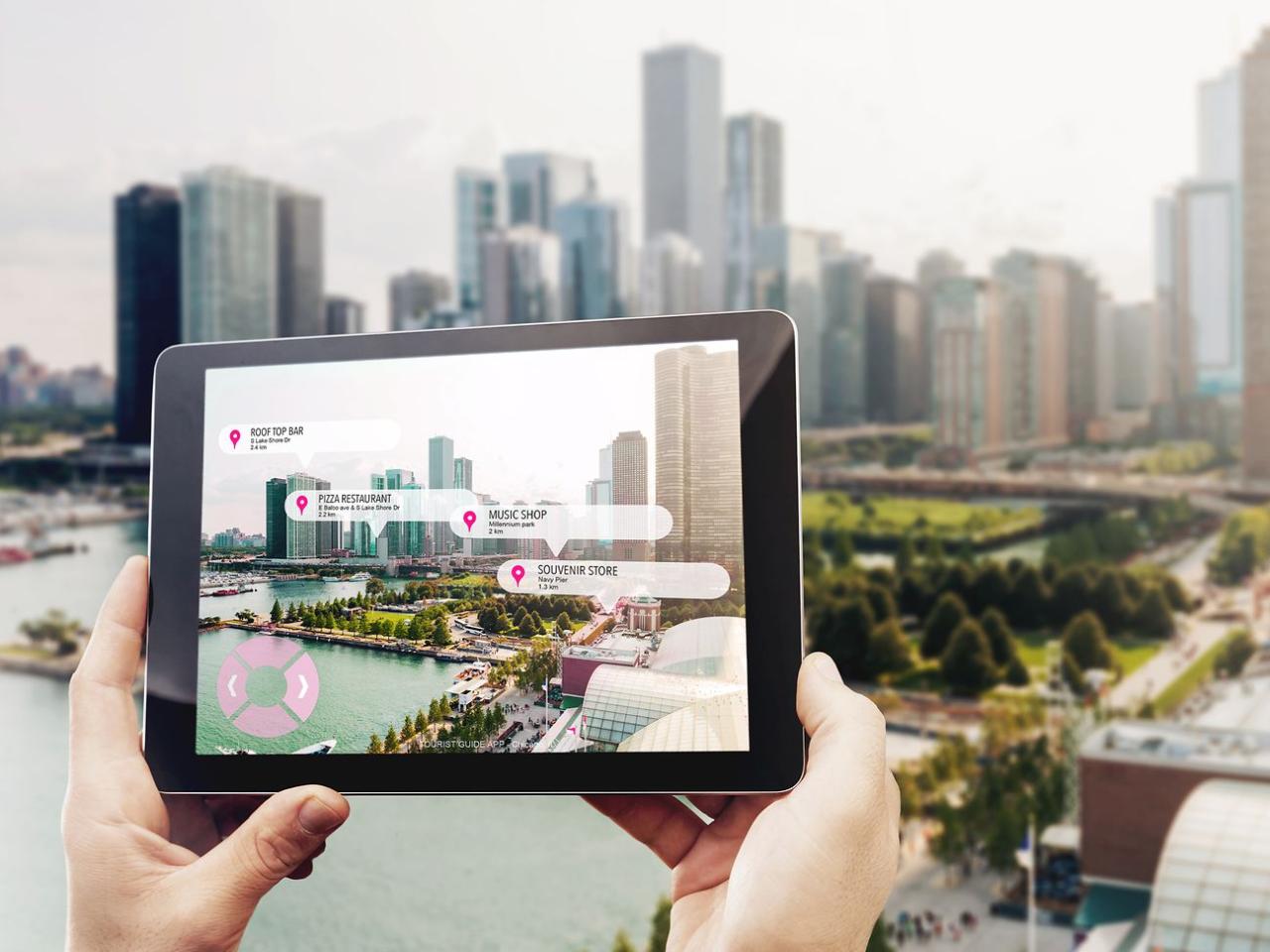
The travel industry is undergoing a technological transformation as augmented reality (AR) evolves from novelty to essential travel tool. This digital revolution is fundamentally changing how travelers interact with destinations, blending physical exploration with digital enhancement to create richer, more educational, and deeply personalized experiences. Unlike virtual reality, which replaces the real world, AR enhances it—overlaying historical reconstructions onto ruins, translating foreign text in real-time, and revealing hidden stories behind ordinary landmarks. This seamless integration of digital information with physical environments is addressing longstanding travel challenges while creating entirely new forms of exploration. From navigation assistance that eliminates the “phone zombie” phenomenon to historical recreations that bring ancient civilizations to life, AR is bridging the gap between convenience and authentic discovery. This comprehensive analysis examines AR’s growing impact across the travel journey, explores implementation case studies, addresses technological and ethical considerations, and anticipates future developments as the physical and digital worlds continue to converge in our travel experiences.
A. The AR Travel Ecosystem: Core Applications and Technologies
Augmented reality in travel encompasses diverse applications powered by increasingly sophisticated technologies.
A.1. Navigation and Wayfinding Revolution
AR is solving the fundamental challenge of navigating unfamiliar environments.
-
Visual Overlay Navigation: Applications like Google Live View and Apple’s AR Walk use camera views to superimpose directional arrows and points of interest directly onto real-world surfaces, enabling intuitive navigation without constant map checking.
-
Indoor Positioning Systems: Advanced AR wayfinding in complex environments like airports, museums, and shopping centers guides users to specific gates, exhibits, or stores while estimating walking time and identifying amenities along the route.
-
Context-Aware Routing: Next-generation systems incorporate real-time data about crowd density, accessibility options, and personal preferences to suggest optimal routes rather than simply the most direct path.
A.2. Historical and Cultural Reconstruction
AR is breathing new life into historical sites and cultural artifacts.
-
Architectural Recreation: Applications at locations like the Roman Forum or Mayan ruins overlay digital reconstructions onto existing ruins, allowing visitors to visualize complete structures as they appeared centuries ago.
-
Historical Event Visualization: Battlefields, significant political locations, and ancient marketplaces use AR to recreate historical events, showing troop movements, historical figures, and daily activities in their original settings.
-
Artistic Restoration: Museums employ AR to showcase damaged artworks in their original condition, reconstruct missing elements of sculptures, or demonstrate artistic techniques through interactive overlays.
A.3. Real-Time Translation and Interpretation
AR is dismantling language barriers that have long complicated international travel.
-
Visual Text Translation: Applications like Google Translate use smartphone cameras to instantly translate menus, signs, and documents, preserving original formatting while replacing text with the user’s preferred language.
-
Audio Augmentation: Emerging AR glasses provide real-time subtitles for conversations and announcements, while experimental systems offer whispered translations during guided tours without disrupting the experience for others.
-
Cultural Context Enhancement: Beyond literal translation, advanced systems provide cultural explanations for unfamiliar customs, gestures, or social situations, helping travelers navigate subtle cultural nuances.
B. Implementation Case Studies: Successful AR Travel Applications
Real-world implementations demonstrate AR’s transformative potential across different travel contexts.
B.1. Museum and Cultural Institution Adoptions
Cultural organizations are leveraging AR to make collections more accessible and engaging.
-
The Smithsonian Institution’s Skin and Bones App: This pioneering application brings skeletal exhibits to life, overlaying animated creatures onto skeletons and providing interactive educational content that has increased visitor engagement time by 47%.
-
The British Museum’s AR Greek Life Exhibition: Visitors use tablets to view AR reconstructions of ancient Greek life, seeing virtual Athenians interacting with artifacts and environments, dramatically improving historical understanding, particularly among younger visitors.
-
The Louvre’s Nintendo 3DS Guide System: This early successful implementation combines AR with gaming elements, allowing visitors to view Mona Lisa recreations and historical contexts while navigating the massive museum more efficiently.
B.2. Destination Marketing and Pre-Travel Experiences
Tourism boards and travel companies use AR to inspire and plan trips.
-
Tourism Australia’s AR Campaigns: Interactive print materials and location-based activations allow potential visitors to experience Australian landmarks and wildlife through AR, increasing destination familiarity and visit intent.
-
Airline AR Cabin Previews: Major carriers enable travelers to use AR to explore seat configurations, entertainment options, and cabin layouts before booking, reducing post-purchase dissatisfaction and support queries.
-
Hotel Room AR Previews: Beyond static photos, hotels offer AR room tours that allow potential guests to visualize themselves in spaces with accurate dimensions and lighting conditions.
B.3. Urban Exploration and Navigation Applications
Cities are developing AR solutions to improve the visitor experience.
-
Seoul’s AR Navigation System: The city government has implemented comprehensive AR wayfinding that overlays directions, public transportation options, and points of interest throughout popular tourist areas, significantly reducing visitor disorientation.
-
London’s Street Museum App: This location-based application overlays historical photographs onto modern street views, allowing users to compare contemporary London with its historical counterparts while learning about architectural and social history.
-
New York City’s ARTIFACT App: This experimental platform uses persistent AR to leave digital notes, recommendations, and historical facts at specific locations, creating a crowd-sourced layer of information accessible to all visitors.
C. Technological Foundations and Requirements
Effective AR travel experiences rely on sophisticated technological infrastructure.
C.1. Hardware Evolution and Accessibility
The devices enabling AR travel experiences are rapidly evolving.
-
Smartphone Dominance: Mobile devices remain the primary AR platform, with advanced cameras, motion sensors, and processing power making sophisticated AR experiences accessible to billions of potential users without specialized equipment.
-
Wearable AR Development: Devices like Microsoft HoloLens and emerging AR glasses promise hands-free experiences but face challenges related to cost, battery life, and social acceptance in public spaces.
-
Location-Specific Installations: Dedicated AR viewers at historical sites and museums provide high-quality experiences without requiring visitors to use personal devices or download applications.
C.2. Software and Content Creation Platforms
The AR ecosystem depends on robust development platforms and content creation tools.
-
AR Development Frameworks: Platforms like ARKit (Apple), ARCore (Google), and ARFoundation (Unity) provide standardized tools for creating cross-platform AR experiences with advanced features like environmental understanding and light estimation.
-
Content Management Systems: Sophisticated backend systems allow destinations to update AR content without reprogramming entire applications, keeping information current as exhibitions change or new research emerges.
-
Cloud-Based Processing: Complex AR tasks like image recognition and 3D rendering increasingly occur in the cloud, reducing device requirements while enabling more sophisticated experiences.
C.3. Connectivity and Positioning Requirements
Reliable AR experiences depend on robust technical infrastructure.
-
GPS and Indoor Positioning Accuracy: Precise location tracking is essential for context-aware AR, with technologies like Bluetooth beacons, WiFi fingerprinting, and visual positioning systems supplementing standard GPS in challenging environments.
-
5G and Edge Computing: High-speed, low-latency connectivity enables complex AR experiences without draining device batteries, while edge computing processes data closer to users for faster response times.
-
Offline Functionality: Recognizing that travelers may lack reliable connectivity, sophisticated AR applications download necessary content in advance or provide degraded functionality when offline.
D. User Experience and Adoption Considerations
Successful AR travel implementation requires understanding user behavior and barriers.
D.1. Interface Design and Usability
Well-designed AR interfaces balance information richness with situational awareness.
-
Information Density Management: Effective AR displays prioritize relevant information while avoiding visual clutter that could overwhelm users or obscure their view of the physical environment.
-
Contextual Activation: The most successful applications activate AR features only when specifically needed or requested, preserving the authenticity of direct experience while providing enhancement on demand.
-
Accessibility Integration: Thoughtful AR design incorporates features for users with visual, hearing, or mobility impairments, such as audio descriptions, haptic feedback, and voice control options.
D.2. Adoption Barriers and Solutions
Despite its potential, AR travel faces significant adoption challenges.
-
Technological Literacy Gaps: Successful implementations offer intuitive interfaces with progressive disclosure of advanced features, avoiding assumptions about users’ technical sophistication.
-
Battery Life Concerns: Power-efficient design, optional low-power modes, and integration with external battery packs address the significant energy demands of continuous AR use.
-
Social Acceptance Factors: Discreet interaction modes and consideration of how AR use affects social dynamics in public spaces help normalize the technology without creating digital barriers between travelers and their environments.
D.3. Experience Balance and Authenticity Preservation
A central challenge involves enhancing rather than replacing direct experience.
-
Optional Enhancement Philosophy: The most respectful implementations position AR as an optional layer that can be ignored by those preferring unmediated experience.
-
Digital Detox Integration: Some applications include features that encourage users to temporarily disable AR enhancements, ensuring technology serves rather than dominates the travel experience.
-
Reality Verification Mechanisms: As AR becomes more sophisticated, features that clearly distinguish historical speculation from documented fact become increasingly important for educational integrity.
E. Future Directions and Emerging Possibilities
AR travel technology continues to evolve with implications for how we experience the world.
E.1. Advanced Personalization and AI Integration
The next generation of AR travel will offer increasingly tailored experiences.
-
Preference-Based Filtering: AI systems will learn individual interests to highlight relevant information while filtering out less relevant AR content based on demonstrated preferences.
-
Adaptive Difficulty and Detail: Educational AR experiences will automatically adjust their complexity and depth based on user engagement and demonstrated comprehension.
-
Social AR Integration: Future systems will enable shared AR experiences where travel companions see synchronized digital content and can collaboratively interact with augmented environments.
E.2. Expanded Sensory Augmentation
AR will eventually engage senses beyond vision.
-
Audio Augmentation Development: Spatial audio will place historical narration, musical performances, and ambient sounds precisely within environments, enhancing immersion without headphones.
-
Haptic Feedback Integration: Wearable devices will provide tactile sensations corresponding to AR content, such as vibrations when approaching significant but invisible historical boundaries.
-
Olfactory Augmentation Experiments: Early-stage research explores scent dispersion systems that release context-appropriate aromas to enhance historical recreations and environmental experiences.
E.3. Ethical and Philosophical Considerations
As AR becomes more sophisticated, important questions emerge about its impact on travel.
-
Authenticity and Mediation Balance: The travel industry must thoughtfully balance convenience and enhancement against preserving direct, unmediated experience.
-
Digital Divide Implications: As AR enhances travel experiences, ensuring accessibility for those without advanced technology becomes increasingly important to prevent a two-tier travel system.
-
Commercialization and Attention Economy: The potential for AR platforms to become advertising channels requires careful management to preserve the educational and enhancement mission of travel AR.
Conclusion: The Blended Future of Travel Experience
Augmented reality represents not a rejection of authentic travel but an evolution of how we engage with and understand the world around us. This technology, when thoughtfully implemented, has the potential to deepen our connections to places, cultures, and history while solving practical travel challenges. The most successful future travel experiences will likely blend physical exploration with digital enhancement in ways that feel natural, respectful, and genuinely enriching. As the technology matures and becomes more seamlessly integrated into our travel habits, the distinction between “real” and “augmented” experience may become increasingly meaningless—what will matter is the depth of understanding, the quality of engagement, and the lasting value of the memories created. The future of travel appears not as a choice between technology and authenticity, but as a sophisticated integration where each enhances the other, opening new dimensions of discovery for travelers willing to see the world through both physical and digital lenses.
Tags: augmented reality travel, AR tourism, travel technology, digital travel, enhanced exploration, navigation technology, cultural AR, historical reconstruction, travel apps, immersive travel, smart tourism, digital wayfinding